Unwanted spam calls, as well as unwanted emails, often come from fraudsters. There are cases when these emails or calls come from companies or stores where you have recently made purchases, orders, etc. But sometimes, the nature of those messages is questionable. Moreover, their amount can make you mad just because receiving a dozen notifications each minute is a bad experience.
What is Spam Calls?
Spam calls are annoying phone calls that contain unacceptable content, obsessive advertising, etc. These can be made primarily by humans and sometimes by robots. But in phone frauds, rascals aim at a more successful outcome of their calls, making them more flexible. That’s why they prefer to call personally and convince users by deception on their adventures. As a result, they can force users to dictate their card number, password, insurance number, confidential information about their place of residence, and the like. If you still talk about robocalls, recorded calls often do not cause much harm. It is usually a reminder of the regular payment for utilities or a survey on the quality of service of the place where you recently visited (for example, in a bank or other institution).
Why am I getting so many Spam Calls?
Users who faced this problem probably wonder – why am I getting so many spam calls. Unfortunately, there are many reasons why users are exposed to spam. One such reason may be your subscription to a questionable website, where you also left your phone number. Then you are automatically exposed to a huge number of calls from unknown numbers and questionable offers. Because of that, we prepared some tips for you on how to stop spam calls.
What are Robocalls?
Automated calling software can make robocalls to millions of people. If someone answers their phone, and it’s not a live person, they listen to a robocall. While some automated calls provide helpful information, such as flight cancellations or reminder messages, most are trying to make money from their recipients. Some of them can even be scams.
How to Stop Robocalls?
To minimize the likelihood of being scammed, heed these tips:
- Immediately put a hang up on any robocalls. Avoid responding to a call or engaging the person on the line. If the other person tries to start a conversation or interact with you, it’s marked as a live call and you may receive more.
- Saying “yes” is to be avoided if possible. People sometimes answer robocalls without realizing that the caller started with a question like
"Hello, can you hear me?"It uses recordings of the"yes"response to commit fraud. So, when answering calls, avoid saying"Yes"if possible. - Report spam calls. The FTC can be contacted via donotcall.gov to report spammers’ robocalls. Reporting the number displayed on a caller’s ID helps the FTC track down scammers. The FTC collects each registered phone number and releases it to the public every business day. Reports help law enforcement identify the individuals behind illegal calls and phone providers working on call-blocking solutions. These reports also help other partners work on call blockers.
How to Stop Getting Spam Calls?
We’ll guide you on how to avoid falling victim to unwanted calls. Get rid of this; you will be able no matter what phone type of operating system you use. So, let’s review how to stop getting spam calls on different devices:
How to Stop Spam Calls on iPhone?
- Go to the App Store and download the app to detect and block phone spam. You can download and install several programs with this feature from different developers.
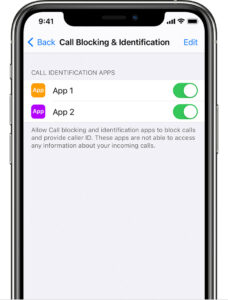
- Go to Settings > Phone.
- Touch lock call and call ID
- Enable or disable the desired application to allow these applications to block unwanted calls and provide the subscriber ID section. You can change the order of transfers according to the priority. To do this, click
"Edit"and drag the programs to display them in order.
How to Stop Spam Calls on Android ?
- On the device, open the application
"Phone." - Tap on the icon
"More"than"settings"then Spam and Call Filter. - Enable or disable Show subscriber ID and spam.
- If you want to block spam calls on your phone, turn on the
"Filter"spam calls"function". You will not receive any missed calls or voicemails, but filtered calls will appear in the call log, and you will be able to check your voicemail.
Spam Phone Calls Revenge
People who receive spam calls threatening them usually ask, “How to you block spam calls and get revenge for this attack?”. There are many ways to punish scammers already available to the public. To combat fraud and run effectively, you need software specifically designed for this purpose.
When a fraudster attempts to sell something, this software typically provides you with a temporary credit card number. That’s a fake credit card number generator so the fraudster can enter its data. Subsequently, the fraudulent sales attempt is rejected by the credit card issuer; however, this information provides you with evidence against whom you can sue.
Receiving spam can cost you money and damage your reputation. As soon as you realize this, it would help if you began taking measures to avoid receiving them in the future. However, it would help if you always were looking for telltale signs that someone is planning to defraud you. Avoid blocking phone-ups that originate from numbers with unclear or unrecognizable numbers. This prevents you from receiving similar phone-ups in the future.
Reminder: Your personal information is protected by laws that no one can break. Therefore, remember to report spam calls and any unauthorized attempts to access your data. Adding an extra app to your phone helps keep unwelcome guests at bay. Therefore, don’t restrict fraudsters’ actions.
How to Prevent Spam Calls ?
After all the mentioned information, you need to know some tips on how to get rid of spam calls and save your privacy and security. The FCC recommends avoiding specific actions to reduce robocalls:
- Don’t answer phone ups from numbers that are blocked or unfamiliar.
- Ignore phone-ups from numbers you don’t recognize.
- Just because a seemingly local phone number appears on the screen doesn’t mean it’s from that area
- Find the company’s phone number on the website or via a personal call from someone claiming to be a company representative. Then, call the number yourself and hang up when someone claiming to be with XYZ company phones you back.
- Do not press a number before speaking to a live representative who shares this same significance.