Users are increasingly encountering malicious links that, when clicked, unleash a different kind of computer destruction. In this case, it is crucial for users to be aware of the appearance of such malware, its associated links, and other potential hazards. This article aims to introduce the concepts of sniffing and spoofing, distinguish between them, explore protective measures against these threats, and delve into their underlying mechanisms.
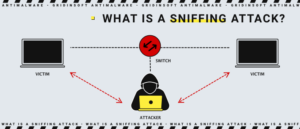
What is Sniffing?
Sniffing involves monitoring data packets and recording network activities. System or network administrators commonly employ sniffers to troubleshoot network issues. However, hackers find sniffing to be a convenient technique. Through sniffing, they can intercept sensitive data packets containing valuable information such as account credentials and passwords. Cybercriminals typically implant sniffer software within the system to facilitate their illicit activities.
Types of Sniffing Attacks
To effectively combat sniffing attacks, it is crucial to understand their origins, characteristics, and defensive measures. Below, we will explore different types of sniffing attacks to provide a clear understanding of their nature and manifestations:
📌 Active Sniffing
Active sniffing occurs within a switch environment. A switch’s primary function is to track MAC port addresses and facilitate data transfer to specific destinations. In active sniffing, interceptors proactively inject traffic into the local network to intercept data between targets. Various methods can be employed to carry out active sniffing.
📌 Passive Sniffing
Passive sniffing involves listening through a hub. When traffic passes through a network segment, it becomes visible to all machines within that segment. The traffic operates at the network link layer. Through this method, hackers send network packets across the network, allowing them to reach connected machines and intercept data.
In the case of active sniffing with address resolution protocols, attackers tamper with the switch’s content-addressable memory tables. By doing so, they intercept data from the switch, redirecting legitimate traffic to alternate ports. Other sniffing techniques include spoofing, DNS, and DHCP.
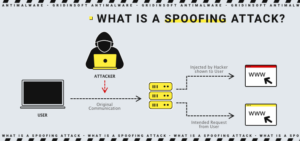
What is Spoofing?
Spoofing is a type of cybercrime where attackers impersonate other computers or networks, disguising themselves as ordinary users to deceive the target into believing the authenticity of the source of information. This method is employed by hackers as a variation of operating system hacking to steal sensitive data, exploit compromised computers, launch DDoS (Denial of Service) attacks, and more.
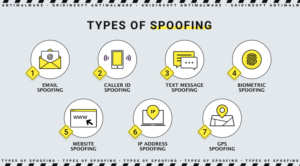
Different Types of Spoofing Attacks
Various forms of spoofing attacks exist, including GPS spoofing, website spoofing, IP spoofing, and others. These attacks target different avenues, demonstrating that attacks and hacks can occur beyond web browsers and pop-up windows. Below, we will outline the most common types of spoofing:
- Caller ID Spoofing. Intruders use spoofing the caller ID so that they can not block the number. They take other people’s numbers; they use alien city codes to disguise themselves. They use voice protocol on the Internet. All this is to get important information from the recipient of this call after the recipient picks up the phone.
- Email Spoofing. Through this method, attackers attempt to steal your confidential data, harm your computer or put malicious software on it. These are disguised emails. The sender’s address bar may seem familiar to you; it is done to deceive you as if the letters were legal. Be careful. In this case, we will use alternative letters or numbers in the sender’s address bar.
- Website Spoofing. Intruders disguise a dangerous website as a legitimate website. They use similar colors and the shape of company logos to do this. The addresses of these sites are also fake, although they may be identical to legal ones. Of course, the primary purpose of this is to harm the user. When you visit such a site, it turns out to be malicious, endangering your computer and its data.
- DNS Server Spoofing. This method redirects traffic to a different IP address. In this case, it occurs at the DNS protocol level. DNS (Domain Name Server) spoofing or DNS cache poisoning is a type of cyberattack used by an attacker to direct the victim’s traffic to a malicious website (instead of a legitimate IP address).
- GPS Spoofing. It’s easy to fool GPS receivers; Fake signals resemble accurate signals. It is done to divert planes, ships, and other vehicles and redirects them to different addresses.
- ARP Spoofing. It is a method of manipulation to capture sessions and steal personal data. The ultimate goal is to access the data of this address’s owner. ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) spoofing is a type of cyberattack that relies on attackers sending malicious ARP packets to a default gateway over a local area network (LAN), using it to associate their own MAC address with an IP address. gateway devise.
- Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attack. They are also known as the attack type «man in the middle» (MITM). In these attacks, the attacker intercepts communication between two users. Thus, the attacker can deceive the victim by revealing confidential information by «substitution» of the identity of the original sender, whom the recipient supposedly trusts.
- Text Message Spoofing. The method of sending a text message via the wrong phone number. These text messages send links through which the user can get malicious and phishing downloads. Protect yourself and your mobile phone data using security.
- Extension Spoofing. The attacker changes the file extension and masks malware under the test file. After running this text file on your device, the malware gets on your device.
Difference Between Sniffing and Spoofing
Now, let’s delve into the distinction between sniffing and spoofing. Sniffing involves the collection of data packets, analysis of network traffic, and the interception of targeted packets. On the other hand, spoofing focuses on stealing user data, distributing malware, and facilitating various forms of data theft through phishing attacks. In spoofing, attackers utilize a foreign IP address and create a TCP/IP connection to deceive the system. In contrast, sniffing occurs when an attacker (or a program) manipulates between two packet transfer points, impersonating one of those points to intercept and steal the data being exchanged between them.
Protection Against Sniffing and Spoofing
Every day, cybercriminals develop more and more different malware for attacks. Below we will consider some of the most common items for protection:
☝ Sniffing
- Install Antivirus Software
- Install VPN
- Do not visit unencrypted websites
- Try not to share WiFi. It may be unsafe
- Do not use unencrypted apps to exchange messages
☝ Spoofing
- Provide packet filtering
- Authenticate systems and users
- Use software to detect spoofing
- Verify the authenticity of the sources
After reading everything, you might be wondering how to navigate online safely. However, this article is not intended to make you fear using various services and withdraw from civilization. On the contrary, our aim is to alert you to the risks posed by cybercriminals and provide you with reliable protection through the use of Gridinsoft Anti-Malware. This powerful tool scans all incoming and outgoing files on your network, actively monitors the websites you visit, and shields you from any malicious attempts targeting your computer. With Gridinsoft Anti-Malware, you can confidently navigate the online world with enhanced security.