With the ever-increasing number of cyber threats, hackers and cybersecurity specialists are taking the initiative. This time, cybercriminals went ahead of the curve. They created a phishing website to coincide with the news that Microsoft was developing a crypto wallet exclusively for its Edge browser. Such a scheme is used to spread Luca Stealer.
Microsoft Crypto Wallet Scam Spreads Luca Stealer
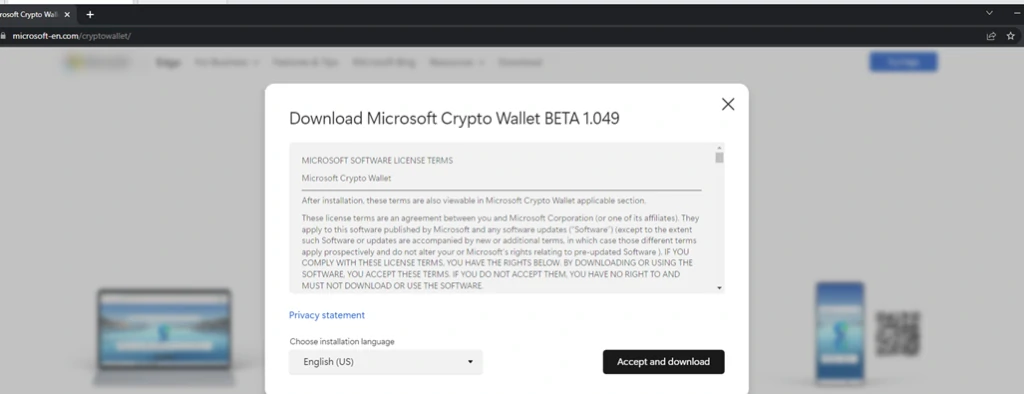
Not so long ago, news broke on the internet that Microsoft is working on creating a crypto wallet for its Edge browser. This news is sure to interest cryptocurrency users. But you know who else is interested in it? That’s right, cybercriminals. The resourceful guys immediately figured out what was happening and created a website that looked as much like Microsoft’s legitimate site as possible. Cybersecurity researchers came across this website and analyzed it. Unlike third-rate phishing sites, this one had a convincing appearance, a web address of hxxps[:]//microsoft-en[.]com/cryptowallet/, SSL certificates, and allknown logic. The website offers the user to download a beta version of the crypto wallet. However, instead of the claimed one, the user received malware.
Luca Stealer Analysis
In this case, the scammers are distributing Luca Stealer. Specialists identified it due to similarities in the malware code found and the Luca Stealer. However, Luca is open source, which users can find on platforms like GitHub or TOR. It is a relatively new stealer, written in Rust and first spotted in 2022. Its job is to collect valuable data such as crypto wallet details and other personal information. The following are the browsers, crypto wallets, and extensions this malware attacks.
Web browsers
| CentBrowser | Iridium | Qip Surf | Chrome Canary |
| Sleipnir 5 | Vivaldi | Elements Browser | CocCoc Browser |
| Torch | Opera Stable | Brave | Kometa |
| Edge | CocMedia | Google Chrome | Mapple Studio |
| CozMedia | ChromePlus | Atom | Chromium |
| UC Browser | Opera GX | WooGamble | Opera |
| Dragon (Comodo Dragon) | Chrome SxS | 7star | Sputnik |
| Epic Privacy Browser | Chedot | Uran | Citrio |
| Orbitum | Chrome |
Browser extensions
| 1Password | Avira Password Manaager | BitApp Wallet | BitClip |
| Bitwarden | BinanceChain | BrowserPass | Byone |
| Clover Wallet | Coin98 | Coinbase Wallet | CommonKey |
| Cyano Wallet | Cyano Wallet Pro | DAppPlay | Dashlane |
| EOS Authenticator | EQUAL Wallet | Guarda | Hycon Lite Client |
| ICONex | KHC | KeePassXC | Keeper |
| Keplr | LastPass | Leaf Wallet | Liquality Wallet |
| Math Wallet | MEW CX | MetaMask | MYKI |
| Nabox Wallet | Nash Extension | NeoLine | NordPass |
| Nifty Wallet | Norton Password Manager | OneKey | Polymesh Wallet |
| RoboForm | Sollet | Splikity | Steem Keychain |
| TezBox | Terra Station | TronLink | Trezor Password Manager |
| Wombat | Yoroi | ZilPay | Zoho Vault |
Crypto wallets
- AtomicWallet
- ByteCoin
- Electrum
- Exodus
- JaxxWallet
In addition to cryptocurrency, malware is interested in banking data such as IBANs. This creates additional risks for those involved in banking transactions.
Data Exfiltration
Once the data is collected, Luca Stealer begins compressing the data for easier transmission. The malware uses the Telegram messaging platform as a covert communication channel. Using a Telegram bot, it discreetly sends stolen data and some statistical information about the stolen data to the operator. It also sends messages to the chat room.
Why Luca Stealer?
Since the source code of Luca Stealer was leaked to the public, attackers can modify it, optimize it and add new functionality. After a more detailed analysis, experts discovered an unusual AntiVM method. Luca Stealer checks the system temperature before starting to execute. Since virtual machines usually generate an error when such a request is made, the malware can understand whether it is on the virtual machine or on a live system. Though, this trick is just about making the analysis longer rather than impossible. It is not hard to make the VM respond properly to the request, returning realistic and consistent temperatures.
Safety recommendations
To avoid unpleasant consequences, we recommend that you follow the following tips:
- Be careful with downloads from the Internet. Download software only from official and reliable sources. If you have any doubts about the authenticity of a website, go to a trustworthy website and make sure that the site you are interested in is genuine.
- Update your software. Sometimes OS updates can be inconvenient. However, this is an essential part as updates contain security patches. To address known vulnerabilities, constantly update your operating system and other software, including browsers.
- Be careful with email messages. According to statistics, email phishing is one of the most effective methods of spreading malware. Do not open suspicious attachments or links in emails from unknown senders.
- Install reliable antivirus software. Use quality anti-malware software and update it regularly to stay protected from the latest threats.
- Educate yourself and stay informed. Unfortunately, in this eternal arms race, cybercriminals are leading. This allows them to create new threats, picking the least predictable forms each time. In turn, cybersecurity experts create effective solutions against them. Study up-to-date threats and deception techniques to be more aware and adapt your actions.


