Strength Adware, a new advertising malware, began appearing on users’ devices. It is still not clear how it manages to get into the system, but its effects are not pleasant. I did a check-up of this malware and can say how dangerous the Strength Adware is.
Strength Adware spreading
The key point of this adware is the attempt to look like a software that helps the PC users to keep their fitness well. It pretends to have the functionality that notifies the user when it needs to have a break and do some physical exercises. At least this information is specified in promotions which were found on the Internet.
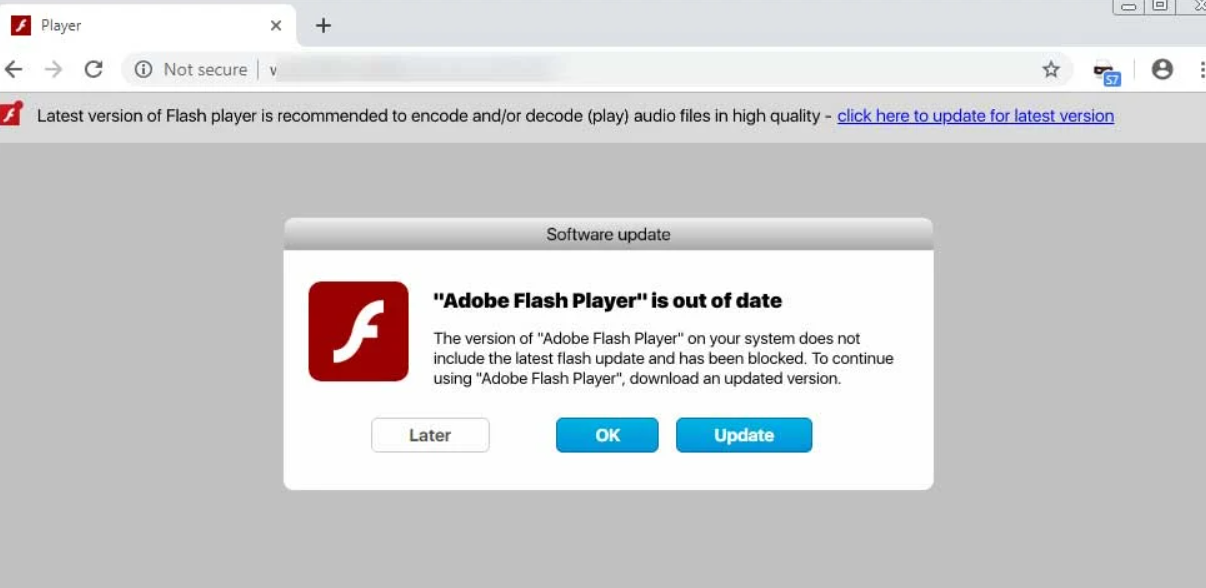
Still, some of the users report about the classic “Update browser” or “Update Flash Player” scam scheme, where the victim is tricked to install adware under the guise of an important update. It is pretty funny since Flash Player has been unsupported since 2021. Overall, this trick is very old and will not likely cease to exist.
What is a Strength App by Strength Tech?
In fact, the Strength app is a classic example of adware. Instead of the functionality it has in its promotion, you will see a ton of advertisements with not very trustworthy offers. They will appear even on the pages that do not have ads by design, and you will not be able to block them with regular ad blocking tools. They are rendered in overlay to the site, so even the changes to the pages’ code will not bring any effects.
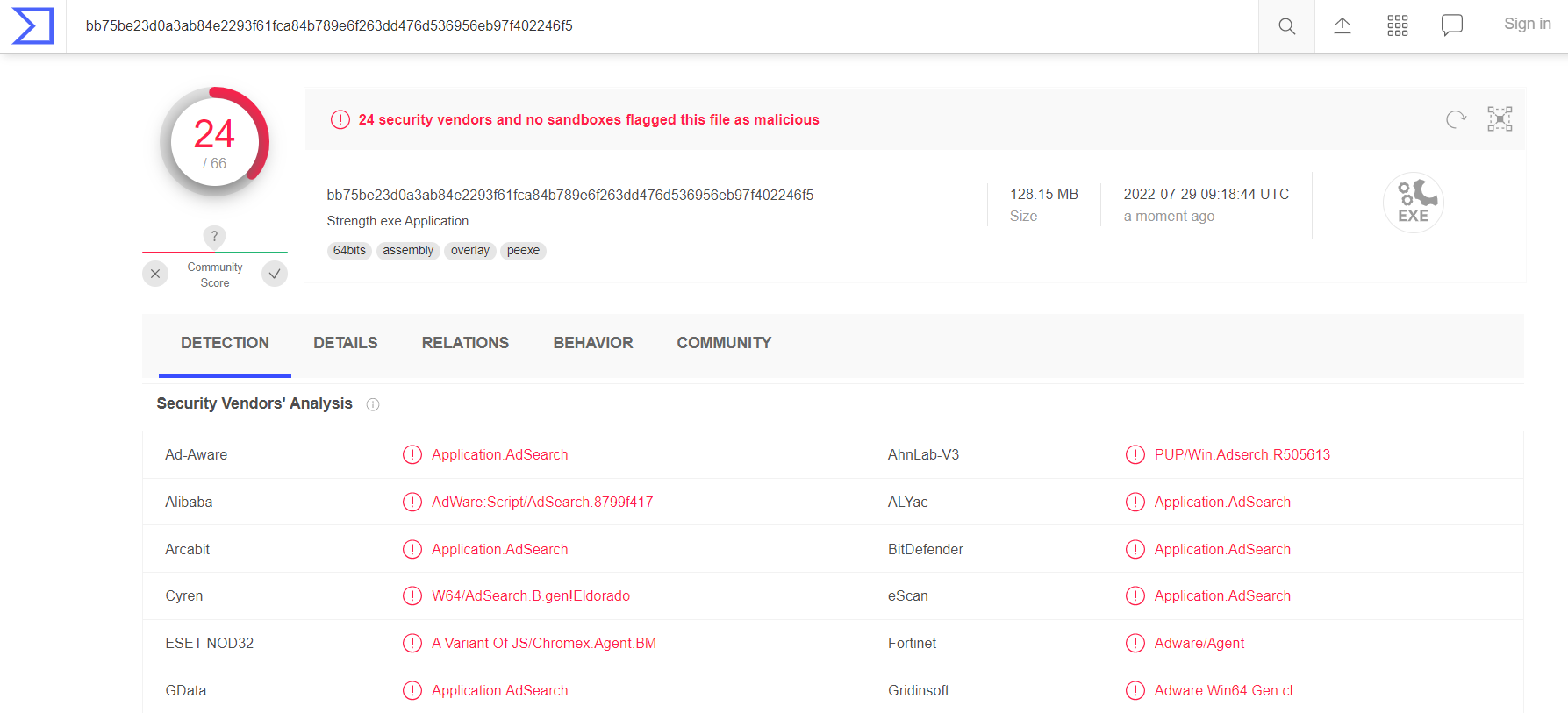
VirusTotal – the worldwide-known antivirus aggregator – confirms the guesses of analysts. Single or several detections could be considered as false alarms, but as you can see, over 20 anti-malware vendors say it is actually malware. Additionally, the site shows that this program contacts two IP-addresses in U.S., without any real need for that action. The creation of registry keys that only aim at launching the app with the system also says a lot about the real intentions of this app. All it tries to do is to show you as many ads as possible, and probably to leak the information about your activities and system to its owner.
Is Strength Adware dangerous?
Like any other adware, it is very unpleasant for your PC, even though it does not expose you to a direct threat. This type of malware creates a sustainable load on your CPU and RAM. For weak systems or thin clients, such a load may be high enough to block any other system functions. But even for high-end systems it is not acceptable to give a certain amount of hardware capacity to junk ads.
But the possible spyware capabilities of the Strength program makes it even a worse thing to tolerate. The more time you give it to function – the more information it can get about your personality. Having a lot of details about you, it is easy to recreate your digital footprint and thus thief your identity. The latter is fraught with money and reputation losses. Removing the Strength Adware as soon as possible is the only proper solution. Try GridinSoft Anti-Malware – it will perfectly fit for malware removal and further protection of your PC.