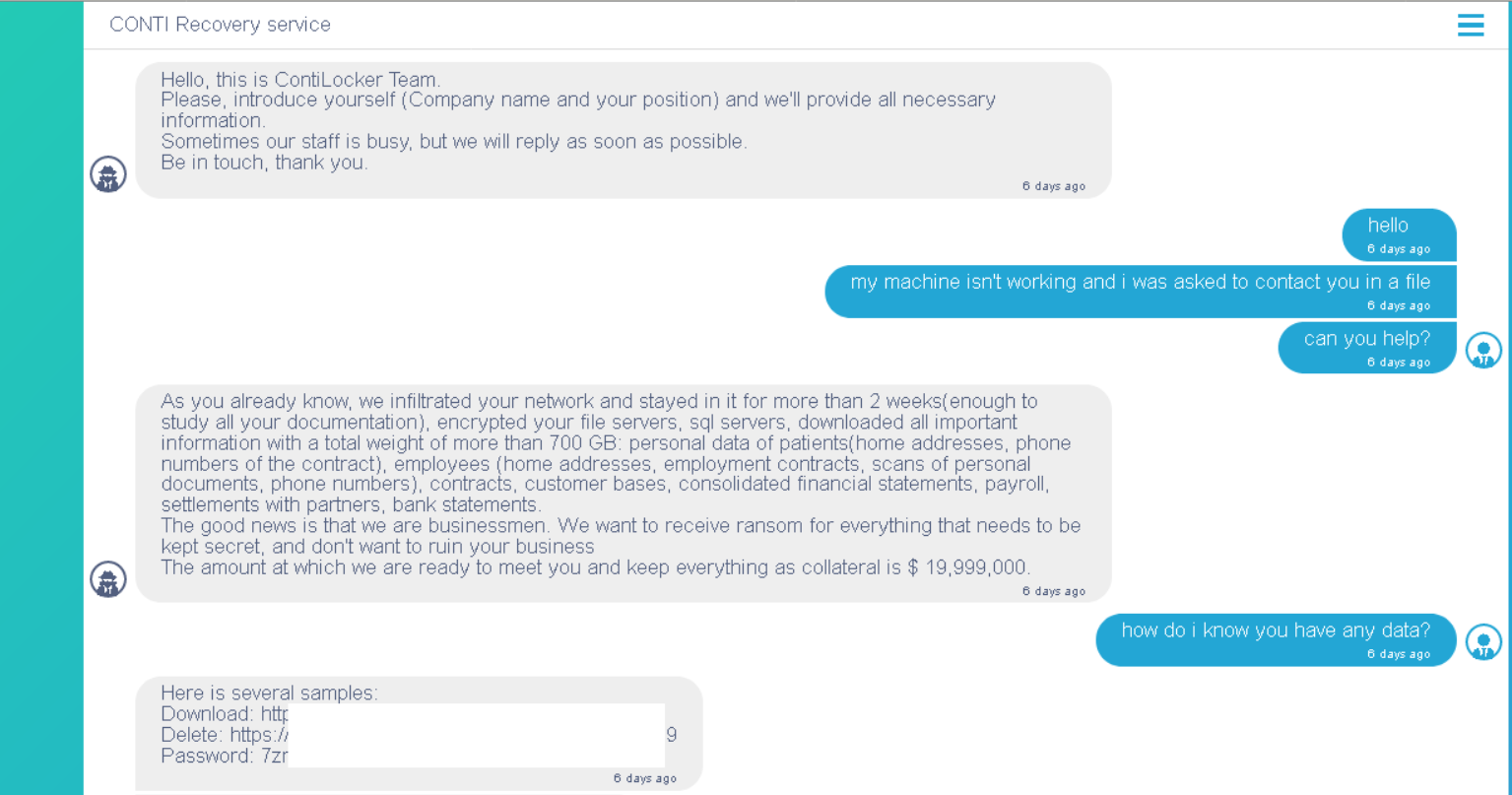
Analysis of more than 40 chats with victims allowed the specialists to figure out some interesting details about the internal structure and the style of negotiation. Conti and Hive ransomware groups were very active over the last quarter, and the number of their victims grew pretty hard.
About Conti and Hive ransomware groups
Those two groups are pretty different in their history and the “fame” they earned in the cybersecurity community. Let’s start with the older one. Conti ransomware was first observed in 2020 – a pretty typical year for most novice ransomware groups. However, a lot of ones have already ceased to exist – by merger, reorganization into other groups and even busting by executive authorities. Conti successfully avoids meeting with men in uniform, generally because of their location – Russia. This characteristic is not axiomatic, but a lot of indirect facts point to that. Conti group is widely known for big ransoms – $850,000 on average, scummy distributors who refuse to give up the decryption key, and ignorance of “ethical hacking” rules accepted by most of the large ransomware groups.

Hive gang is younger – its activity was first observed in August 2021. They reached their peak activity in November, with 429 attacks out of 1264 in total (as of February 2022). It is worth noting that the programs they use in their attacks are pretty advanced – they can freely work in Windows as well as *NIX systems. The latter is a great trump against the companies who use Linux distros on a continual basis and ignore any cybersecurity measures for computers in the network. Same as Conti, Hive ransomware group attacks the “whitelisted” companies with no clue to the agreements. There were 125 attacks on healthcare institutions, 38 on education, and 8 – on governmental organizations registered in 2021.
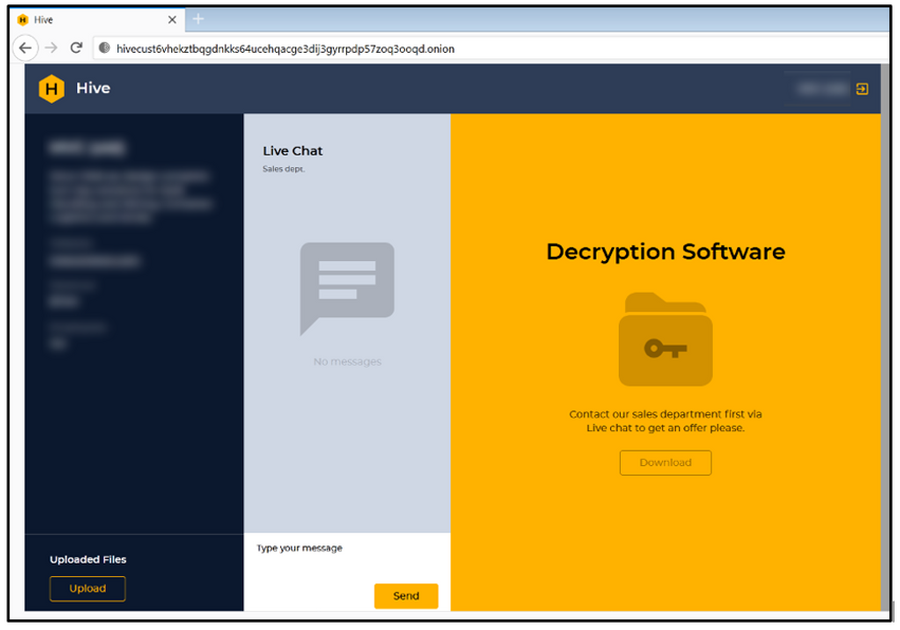
Besides the different histories, groups have some elements in common. As you can already see, they ignore the tacit ban on attacking healthcare and governmental institutions. Also both groups practice a so-called double extortion technique. It is the case when crooks ask for a separate ransom for data decryption and keeping the stolen files unpublished. In total, these groups create almost 30% of all ransomware attacks during the last 4 months.
Analysis of the Conti and Hive groups’ conversations
Having a look at any conversation may uncover interesting details not only about the person who was talking but also about the overall policies. The other thing these groups share is that both of them are decreasing the demanded sum pretty easily. However, the other aspects of their talks differ a lot.
Conti acts as professionals – no spare words, no excessive text
Conti group operators sometimes even practice triple extortion techniques. The third object for asking for the ransom is the reputational losses. Cybercriminals push on the victims to force them to pay all three. Otherwise, they will publish the information about the security breaches in the company. That’s why, exactly, the average ransom of the Conti group is so big. However, there is also a nice moment – they offer the victims to get an “IT-support”, with a detailed report on vulnerabilities used in the attack and detailed guidance on how to avoid further attacks. Conti operators also never stand strictly for the payment timings, offering the company to choose when and how it will pay. Gangsters from this group are opportunistic, attempting to get at least one payment rather than getting nothing at all. Overall, Conti group operators act in a formalized manner – with patterned responses and depersonalisation of the agent.1
Hive group prefers an informal, non-formalised talk
Hive group, on the other hand, has a much more linear approach to the conversations. Despite being open to talks on ransom sum decreasing exactly after the attack, they quickly increase the ask after the designated term expires. It is also worth noting that the ciphering module the Hive group uses aims at encryption speed. Simultaneously the reliability of this system decreases significantly. Therefore, the errors in the encryption may be used to recover the master key. Such a key fits all devices in the corporations that ransomware has touched. Most likely, they wish to scare the victims with a bigger sum is dictated by that flaw.
Another thing analysts have spotted about the Hive group is that they did not follow any kind of standard procedure. They chat with the victims as if they were just their pals, with no straight policy on answers and questions. Hive operators freely uncover the details about their ransomware toolkit – encryption methods, injection ways – they don’t keep it a secret. Is that a conscious policy, or just a recklessness of people who work in this group – no one can say for sure. But this looks much less professional than the approach the Conti group uses.
- The detailed review of the conversations from the Cisco Talos group.