Funny Tool Redirect is a malicious browser extension that you may see installed in your browser. It spreads through dodgy websites and does a rather unusual mischief: blocking access to the Chrome Web Store. While being not a big deal at a first glance, its unwanted appearance, along with other extensions (like JsTimer) that spread in that way makes the situation concerning.
Malicious browser extensions are far from being a new type of threat. Nonetheless, 2024 seems to be the year of their comeback as a widespread and rather potent cybercrime tool. During the unwanted redirect they are mainly known for, such extensions may also collect a lot of user information. This eventually makes the situation much more threatening for the user, primarily on the part of privacy.
What is a Funny Tool Redirect Extension Virus?
Funny Tool Redirect is a browser extension for Chrome and Chromium browsers that falls into a category of malicious plugins. Its visible behavior is not too threatening on the surface: all it does is redirect the user to the main page of Google Search should they try opening the Chrome Web Store. The way it works is pretty simple: it can track the URLs that the browser tries to open and simply intercepts every single call to the chromewebstore.google.com website. That functionality is identical to what browser hijackers can do.
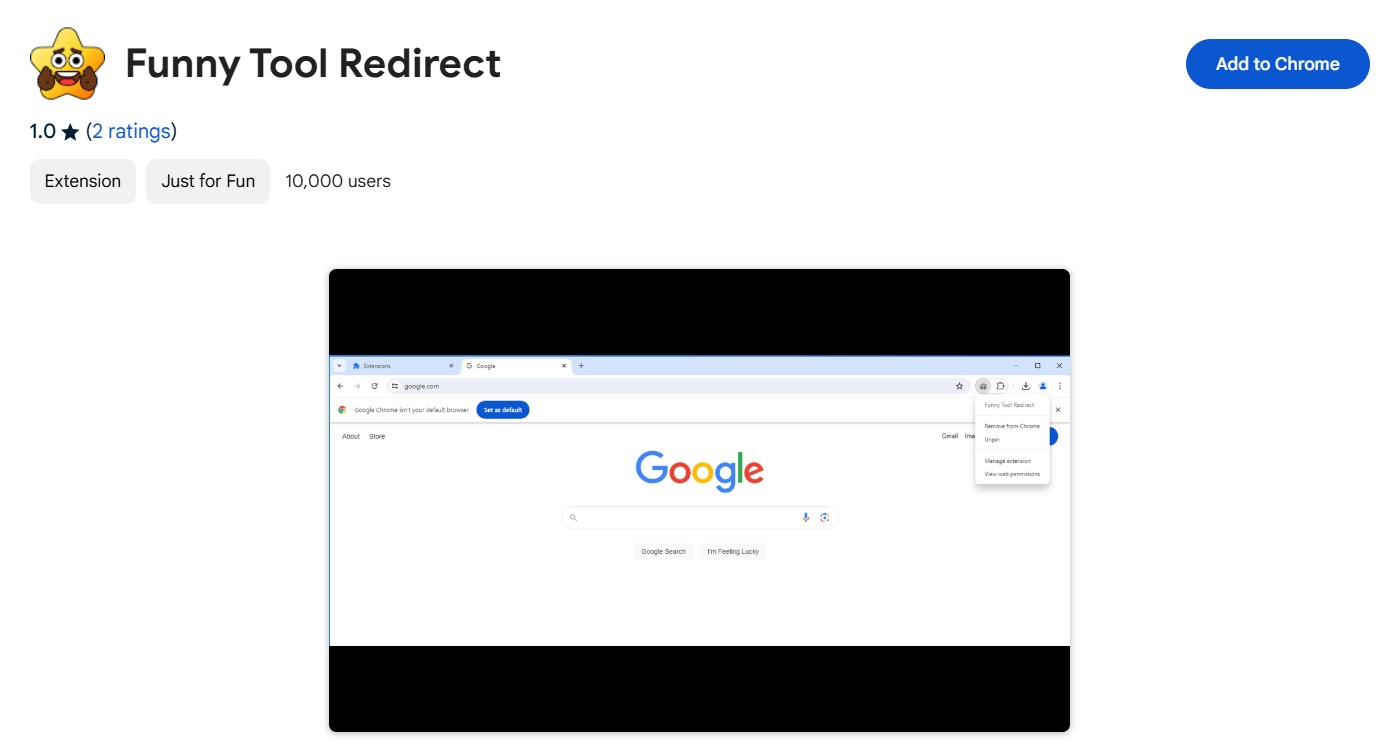
Similar to all other extension viruses, Funny Tool abuses the “Managed by your organization” feature of Chromium browsers. As the name goes, this mode normally means that the company has set the browser up, and protects the extensions and other settings from user modifications. But in this case, con actors who design the extension take advantage of this feature to prevent manual removal attempts.
Effects of a Malicious Plugin
The Funny Tool Redirect browser extension appears to have distinct behavior depending on the IP address of the computer. It works in a rather simple manner: if the system is in the region from the “operational” list, it will go to its mainstream behavior. However, should the extension detect any of the “banned” country IPs, the behavior switches to a much less harmful mode.
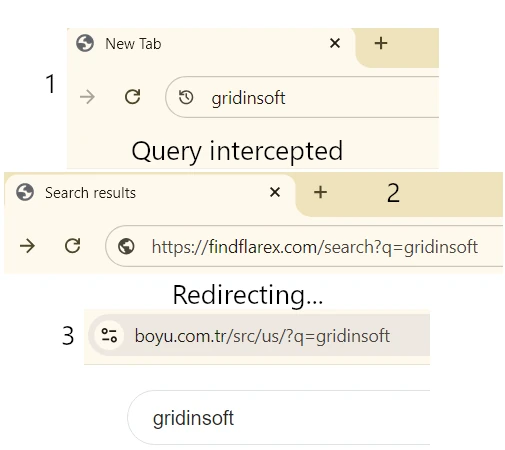
So, the main activity of Funny Tool Redirect is redirecting the user from any Google search requests to a different search engine. In its current iteration, it routes everything to findflarex.com, which further throws the user to boyu.com.tr. The former is an intermediary website that, aside from intercepting the original request, also injects additional search tokens. The latter, in turn, is a wannabe search engine that uses the said search tokens to display huge amounts of ads. All this eventually forms the monetization form for that malicious scheme.
Another part of this scheme is blocking access to the Chrome Web Store. You see, people can get disgruntled with a thing that hijacks their search queries. The obvious reaction is to find the mischievous extension in the Web Store, leave a bitter comment, and report abuse to the administration. What the plugin does in this case is redirecting any requests to chromewebstore.google.com to the main Google page. This may look like not too much at first glance, but in combination with other malicious actions, it brings up a lot of problems.
When Funny Tool Redirect sees the “wrong” location of the system, it will only block the user out of the Chrome Web Store. Such tactics may remain unnoticed, if the user does not visit the store quite often, but may still be useful for other malicious extensions.
Spreading Ways
Most of the time, junk extensions like Funny Tool Redirect get into a user device through a fraudulent website that the user is getting redirected to. The latter often happens during interactions with questionable sites, typically ones with pirated content. On the page, the user sees an offer to install “the recommended extension” (text may vary depending on the case). Hackers’ hopes are on people clicking through the pages in a rush to get to the desired content. And that is it – after a single session on such a website, a user may end up with a handful of malicious extensions.
Another often situation that leads to the “install the extension” page is when there is an active adware in the system. Aside from injecting ads into all the pages that the user visits, it may also open additional tabs with more ads, or other questionable content. And since malware actors often stick to working with each other, it is not a big surprise to see adware opening a malicious extension installation page.
How to Remove Funny Tool Redirect Extension?
It is possible to get rid of Funny Tool Redirect in both manual and automated ways. I will recommend sticking to the automated due to the matters I’ve described above. Source malware, as well as other junk that could have gotten into the system in the same way will remain present even after you remove the extension. And for this purpose, I recommend you to use GridinSoft Anti-Malware.
Download and install Anti-Malware by clicking the button below. After the installation, run a Full scan: this will check all the volumes present in the system, including hidden folders and system files. Scanning will take around 15 minutes.
After the scan, you will see the list of detected malicious and unwanted elements. It is possible to adjust the actions that the antimalware program does to each element: click "Advanced mode" and see the options in the drop-down menus. You can also see extended information about each detection - malware type, effects and potential source of infection.
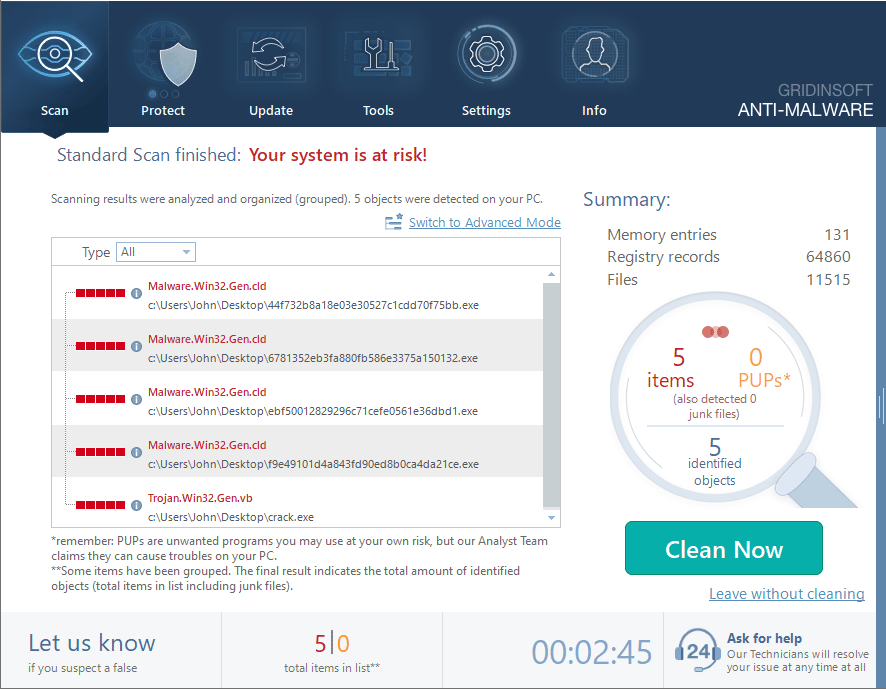
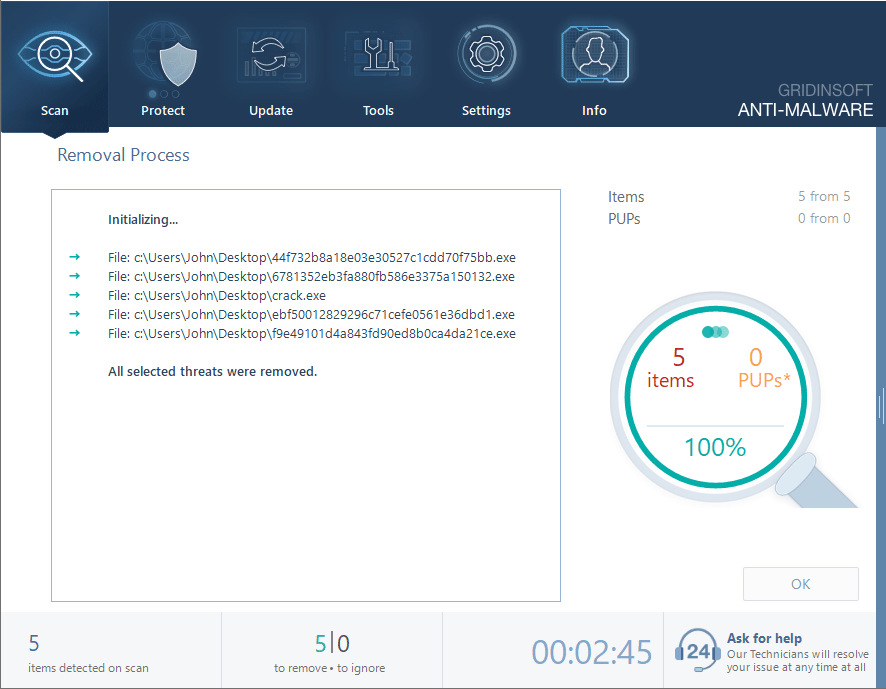
Click "Clean Now" to start the removal process. Important: removal process may take several minutes when there are a lot of detections. Do not interrupt this process, and you will get your system as clean as new.
Manual removal method
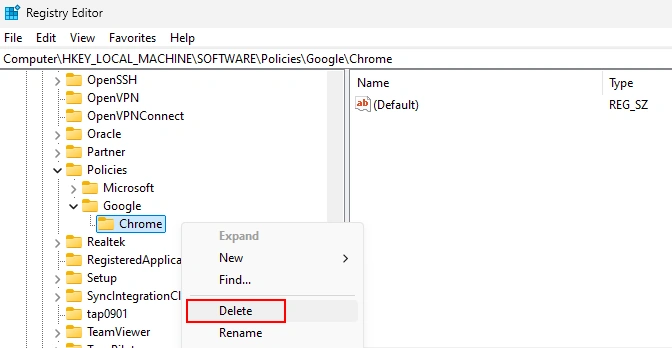
To get rid of the Funny Tool Redirect extensions manually, you will need to get rid of the “Managed by your organization” thing. This trick stems from changes in the browser’s registry keys that are responsible for such deep configurations. Removing that registry key will do the job. Open Registry Editor by pressing Win+R and typing “regedit” into the appeared window. There, paste the registry address you see below:
Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Google\Chrome
You should delete this registry key: click it with the right mouse button and choose the corresponding option. That shall do the job – thereon, nothing will block you from removing the extension through the extension tab. After starting up, Chrome will recover its registry key, but without the malicious change.
You can also see the guides online that offer to change Group Policies. I will not share it here, as it is not possible to accomplish for all users of non-Pro Windows editions. And that is just another reason why removal with anti-malware software is preferable.
Thank you so much! the registry steps worked for me. Got it while downloading some files. Thx for help!