BlackGuard, a prolific infostealer malware, received an update at the edge of 2023. The new update introduced advanced data-stealing capabilities and secure connectivity features. The new version also includes a row of new anti-detection and anti-analysis capabilities. Let’s have a more detailed look into this malware and see the difference from all aspects.
BlackGuard Stealer – What is it?
BlackGuard is a classic infostealer malware, programmed in C#. It aims at grabbing personal data from web browsers, particularly seeking data related to cryptocurrency wallets. It first appeared in 2021, being promoted both on Darknet forums and in a dedicated Telegram community. A lifetime subscription for this malware costs $700, while a monthly subscription is available for $200. Its promotion campaign saw a major boost in 2022, when its competitor Raccoon went for a hiatus.
From its beginning, BlackGuard was aiming precisely at stealing crypto credentials, and this remained its bearing point in further updates. November 2022 patch brought overall improvements to the way malware gathers cryptocurrency-related data, but also introduces the ability to load other malware, i.e. act as a dropper. Patch notes published in the Telegram community contain information about a pack of other changes, mostly related to C2 connectivity.
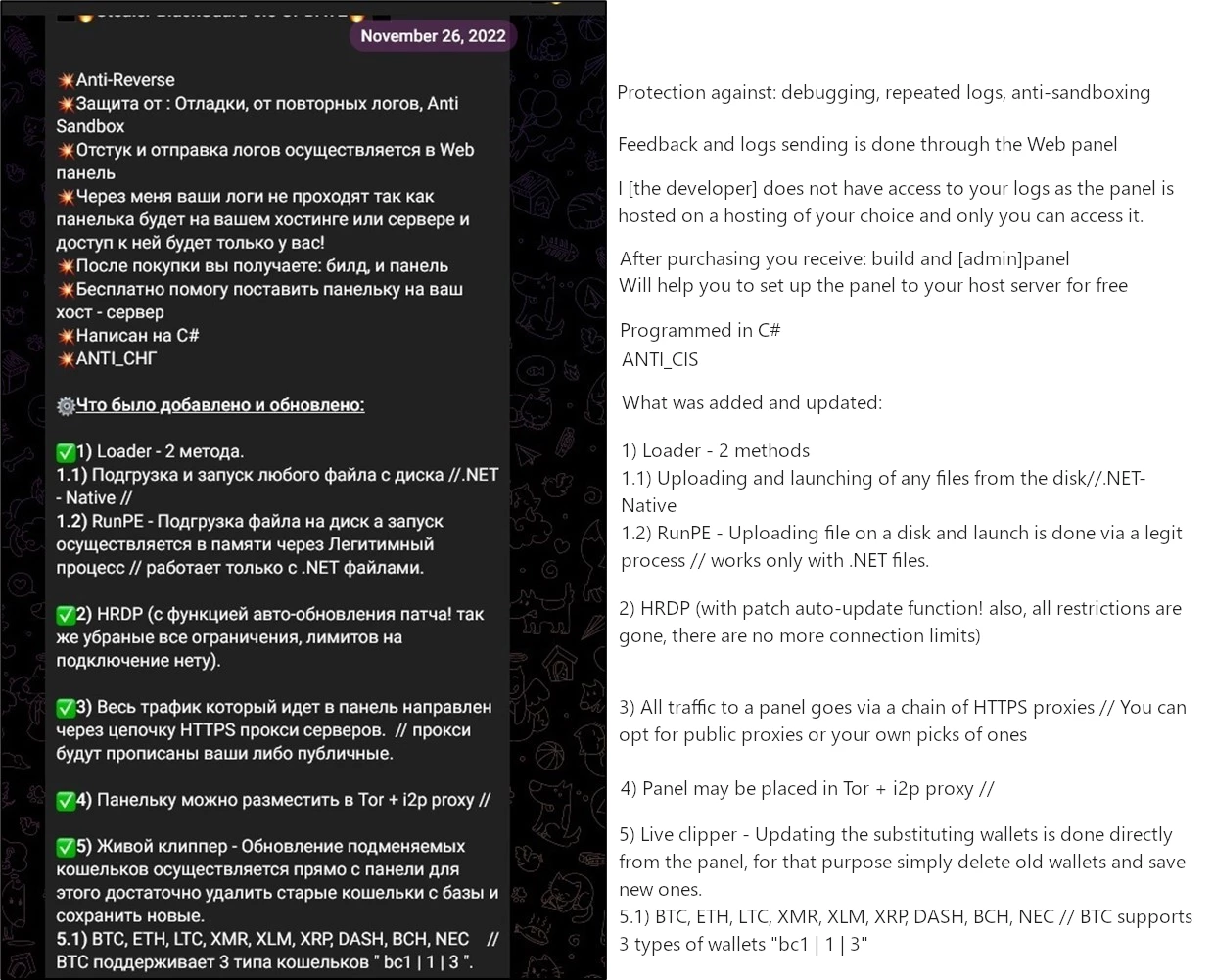
Anti-analysis tactics
First notable thing about BlackGuard malware is its anti-analysis measures. BlackGuard typically arrives at a target device in an encrypted form. The encryption is done by a tool embedded into the admin panel of the malware. Additionally, its code is obfuscated in a pretty specific manner: base64-encoded strings are getting decoded only during the runtime. But even before the decoding, the strings are represented as an array of bytes – a completely unreadable one. Such a practice appears to be pretty effective against anti-malware programs that try to analyze the strings.
Malware also checks the computer name, seeking a match with the hardcoded list it brings among its code rows. These are the names typically applied to virtual machines or live systems used in virus analysis. If the one is detected, BlackGuard will cease any further execution. Debugging, however, also receives its treatment – malware can block any inputs if it detects the activity of a debug tool. Typically for all malware developed in Russia and ex-USSR countries, , this stealer refuses to run in ex-USSR countries.
Data stealing
Once all the checkups are passed, the malware starts its main course – credentials stealing. As I mentioned above, BlackGuard’s primary target is login information contained in web browsers, and one related to cryptocurrency wallets both as a browser extension and desktop application. It seeks the AppData/Local folder for the directories that belong to web browsers and applications. All the gathered data is located to a folder where malware is launched (usually Users/Temp). Before sending to a command server, malware packs that data into a protected .zip archive. It brings the password among its code rows.
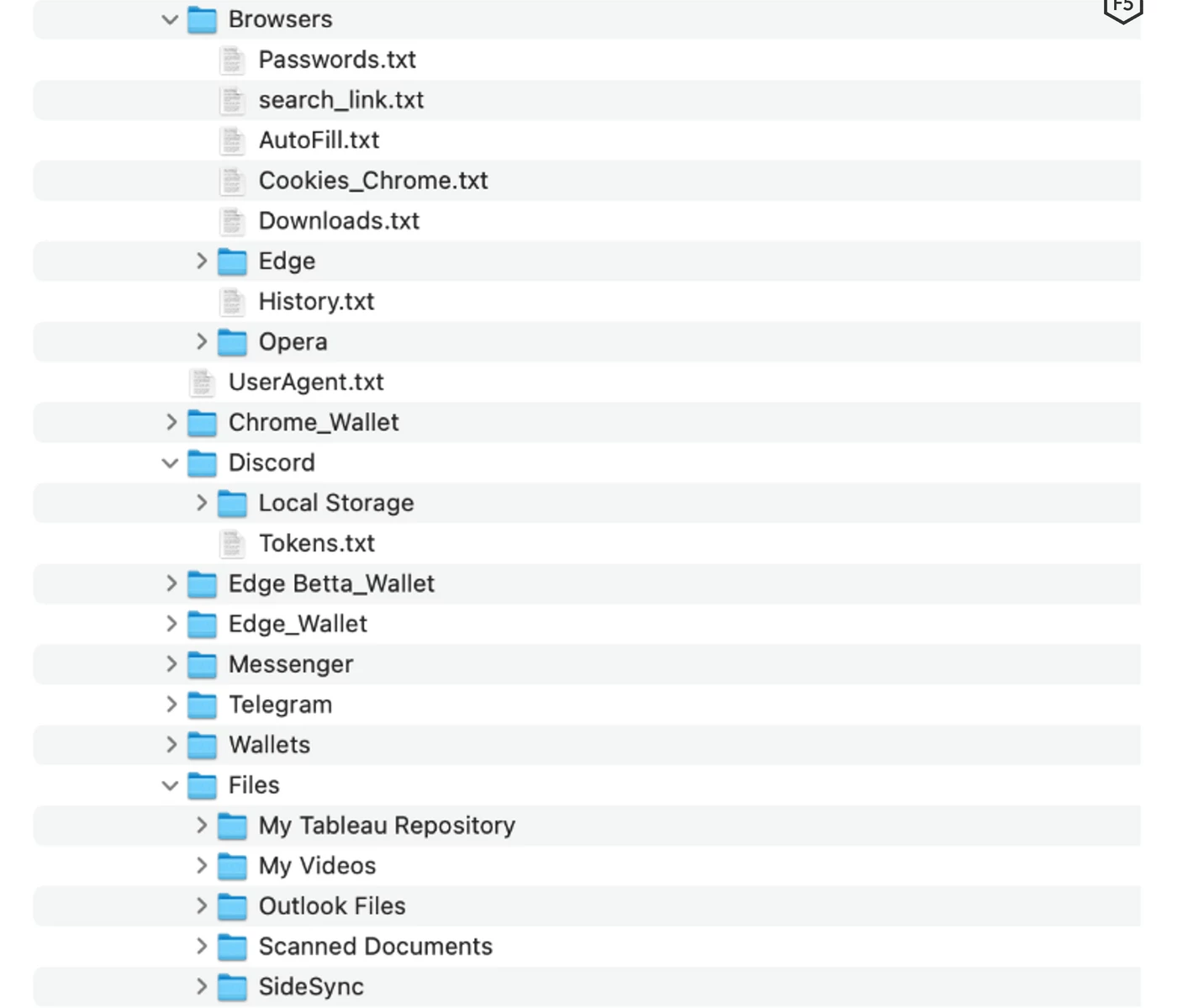
List of web browsers attacked by BlackGuard
| Chrome | Opera | Firefox | Edge | Iridium | 7Star |
| CentBrowser | Chedot | Vivaldi | Kometa | Elements Browser | Epic Privacy Browser |
| Sputnik | Nichrome | K-Meleon | Uran | liebao | CocCoc |
| MapleStudio | BraveSoftware | Chromodo | uCozMedia | QIPSurf | Orbitum |
| Comodo | Coowon | Amigo | Torch | Comodo | 360Browser |
Crypto wallets attacked by BlackGuard
Desktop applications
| AtomicWallet | AtomicDEX | Exodus | LitecoinCore | Monero | Jaxx |
| Zcash | BitcoinCore | DashCore | Electrum | Ethereum | Solar |
| Wassabi | TokenPocket | Frame | Zap | Binance | Coinbase |
Browser extensions
| Binance | KEPLR | coin98 | Mobox | Metamask | Phantom |
| BitApp | Starcoin | Slope Wallet | Finnie | Guildwallet | iconx |
| Swash | Crocobit | XinPay | Sollet | Auvitas wallet | Math wallet |
| Yoroi wallet | Ronin wallet | MTV wallet | Rabet wallet | ZilPay wallet | Terra Station |
| Nifty | Jaxx | Liquality | Math10 | Exodus | OXYGEN |
Other application
Additionally, BlackGuard is capable of collecting credentials from a row of VPN clients and FTP/SFTP utilities, desktop messenger apps, and Microsoft Outlook. Particularly, it grabs credentials from configuration files of NordVPN, OpenVPN and ProtonVPN. Steam and Discord are hacked in a similar manner, while Tox, Signal, Pidgin, Telegram and Element are getting all the conversation collected.
How to protect yourself?
There is only one consistent spreading method used by threat actors who operate BlackGuard – email spam. The latter, however, will likely have a form of spear phishing, that tries to resemble genuine mailing or even messages that its victim is waiting for. Most of the time, crooks gather information using OSINT about their victims for some time before sending messages.
The exact message contains an attached file, commonly an MS Office document. However, any file that can carry executable contents may be used. Office files gained popularity as VBS macro scripts they can carry is ignored by the vast majority of anti-malware software. Launching the file makes the script run: it contacts the command server, downloads the payload, and runs it. This obscenely simple scheme was disrupted by the introduction of Mark-of-the-Web. Using the latter, Microsoft marks potentially risky files, calling additional attention to anti-malware programs. Still, that feature is present only in the latest Windows versions, and as it usually happens, users do not haste to install it.
Another piece of advice to follow is to use anti-malware programs. Hackers do their best to make you believe the spam email or banner online. For that reason, it is better to exclude the human factor by using an automated solution that will not be fooled. But to be sure that such a sneaky thing as BlackGuard will not slip through, it is important for the security tool to have multi-layer protection. GridinSoft Anti-Malware can offer this to you – the program features a “classic” database-backed scanning, as well as a heuristic engine and AI-based detection system. All of them together create a reliable shield even against the most modern – and potent – threats.