The modern business world has been greatly advanced by the internet. Its convenience and numerous benefits have made people from all over the world reliant on the digital world. As the use of digital platforms continues to increase, businesses of all sizes should consider their digital footprint.
What is Corporate Digital Footprint?
Your company’s digital footprint encompasses all its online activities, transactions, communications, marketing, and networking. This also includes those of your business partners, such as vendors and suppliers. The cloud has complicated digital footprints in recent years as it’s used for mission-critical operations, expanding their digital footprints and making them harder to define or secure. However, managing and securing your digital footprint is achievable as long as you know how to begin.
Company’s vs. Person’s Digital Footprint
A company’s digital footprint and a person’s digital footprint differ in identity, target of attacks, data volume, and consequences. For example, cyberattacks on personal digital footprints aim to compromise personal information and financial data. Conversely, attacks on a company’s digital footprint target information systems and sensitive data. Since attacks on a company’s digital footprint are more complex, they have severe consequences. It can be a loss of customer trust, financial loss, and legal problems. Understanding these differences is crucial in developing appropriate security measures to protect personal information and digital infrastructure.
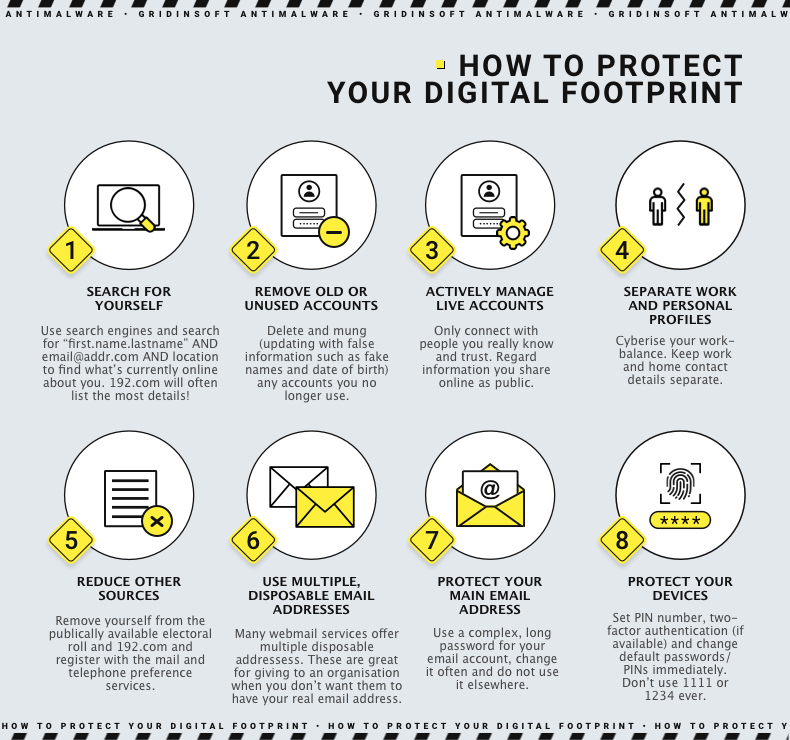
Types of Digital Footprint Risk
To simplify the complex digital risk landscape, it can be divided into categories. This will assist organizations in pinpointing the most vulnerable areas of their systems and providing targeted risk protection. There are nine main categories of digital risk:
- Data Privacy. Sensitive data risks refer to any potential threats that could compromise the protection of confidential information, including personally identifiable information, financial data, and more.
- Cybersecurity. Risks associated with unauthorized access to sensitive resources and potential data breaches. These risks may be inherent or residual.
- Data Leaks. Accidental exposure of private data, known as data leaks, can potentially lead to data breaches. With the expansion of the digital landscape, there are more instances of data in use, data in transit, and data at rest. Maintaining data security is challenging under these dynamic conditions, making data leakage an unfortunate consequence of digital transformation.
- Compliance. Non-compliance risks pertain to violating regulatory compliance standards, which can lead to malpractices. Failure to comply by vendors can also impede digital risk protection efforts. Several regulatory requirements mandate complete compliance.
- Third-Party Risk. Understanding the potential risks of working with third-party vendors is essential. These risks may include vulnerabilities within the vendor’s ecosystem, breaches of security measures, failure to comply with regulations, and even theft of intellectual property.
Cloud Technology. Some risks can affect systems, processes, and people. These risks can arise from technological incompatibilities, errors, and failures. - Process Automation. Compatibility issues can occur when automation processes are changed or new functions are added. These issues may also affect technology risks.
- Resilience. It means maintaining critical services and operations during disruptions or risks. Risks can include server outages or data breaches. Lack of backup and recovery systems, redundant infrastructure, and disaster recovery plans to minimize downtime and restore services can paralyze an organization indefinitely.
How To Protect Your Organization’s Digital Footprint
To prevent cyber attacks, it is essential for businesses to first identify the threats. This allows them to determine what needs to be protected, how to protect it, and what risks to watch for. In a nutshell, the main issues that should be on the agenda are: “What methods are hackers currently using to attack?“, “What is encryption?“, “How can our staff spot a phishing email?“, “Are our software programs up-to-date?“, “What are our vulnerabilities?“, “Is our data stored securely?” et cetera. By staying informed, businesses can better protect themselves against cyber threats. In the following, we will look in more detail at five methods to reduce the risks.

Attack Surface Exploration
Everything is online these days. Virtually any firm or business has a website showcasing its products or services. Users can find hundreds of Web sites for everything from company to manufacturing to commerce to education to entertainment. Digital access is undoubtedly convenient, but IT professionals know it increases the risk of cyberattacks. Rapid expansion into new environments leads to technology sprawl. As a result, misconfigurations and lack of visibility increase security risks and vulnerabilities. Of course, attackers take advantage of this. We saw, during the pandemic, as many technologies were deployed hastily. As a result, many exploits targeted load balancers, cloud environments, and VPNs. However, you can increase visibility by applying some tactics, among them:
- Monitoring the latest threat intelligence and trends to understand evolving risks
- Maintaining an up-to-date asset inventory of systems, networks, applications, and devices to identify potential entry points
- Conducting regular vulnerability assessments and penetration testing exercises to find weaknesses and potential attack vectors
- Educating employees and stakeholders about cybersecurity best practices to reduce human error
- Performing thorough vendor risk assessments and monitoring the security posture of third parties as part of a holistic third-party risk management program
Using these tactics, you can strengthen your security posture and protect your valuable data.
Fast Discovery and Reaction to Vulnerabilities.
Vulnerability assessment provides a snapshot of security vulnerabilities. However, vulnerability management is a continuous process that offers real-time remediation guidance. The former involves using scanners to identify known vulnerabilities. At the same time, the latter employs multiple data sources to continually assess the situation. Vulnerability assessments identify outdated applications or operating systems and device configuration issues such as insecure ports and weak passwords. They are best suited to detect common vulnerabilities and exposures, or CVEs, listed in publicly available databases.
You can consider these six steps a continuous cycle, not a linear process. Firstly, make an asset directory and inventory all assets. Classify them by risk level and prioritize them. Arrange them based on exposure to vulnerabilities and build a security strategy. Remediate the prioritized vulnerabilities and evaluate the security strategy’s effectiveness. However, you can use continuous vulnerability scanning tools. These solutions can automatically monitor your networks, systems, and applications, quickly detecting weaknesses such as:
- Open ports
- Misconfigurations
- Outdated software
Combining this strategy with other tactics mentioned earlier will enable you to proactively identify hidden vulnerabilities, prioritize them accordingly, and allocate resources effectively to minimize risks.
Performing Cybersecurity Analysis to Find Weaknesses.
Identifying security risks and vulnerabilities is crucial to determining their root cause. By doing so, you can gain insight into the underlying factors that led to the issue and implement adequate preventive measures to avoid similar problems. It also helps to prioritize remediation efforts, allocate resources effectively, establish accountability, and improve incident response procedures. You can achieve this by conducting thorough incident investigations, analyzing system logs, and performing forensic analysis.
In addition, Business Impact Analysis (BIA) is crucial to business continuity planning. It involves identifying critical business functions and assessing their dependencies, determining Recovery Time Objectives, assessing impact, conducting a risk assessment, and developing mitigation strategies. The goal is to understand vulnerabilities, dependencies, and potential consequences of disruptions, enhancing resilience and ensuring the continuity of critical operations during adverse events. This will help not only with finding weak spots, but also motivation to improve your business’ cybersecurity.
Spot third-party risks.
According to analyses, supply chain attacks are now the most commonly used method by threat actors to access networks. Thus, research indicates that 62 percent of network intrusions stem from a third party, typically someone in your digital supply chain. Moreover, if a third-party system is breached or compromised, this can have serious consequences. It can include data breaches, service outages, and reputational harm. To prevent cyber threats, it’s essential to proactively identify third-party cyber risks, assess vendor security practices and controls, and take appropriate measures to reduce risks. Best practices in this area include:
- Conducting thorough security assessments.
- Implementing contractual agreements that enforce security requirements.
- Regularly monitoring third-party security practices.
- Establishing incident response protocols in collaboration with your vendors.
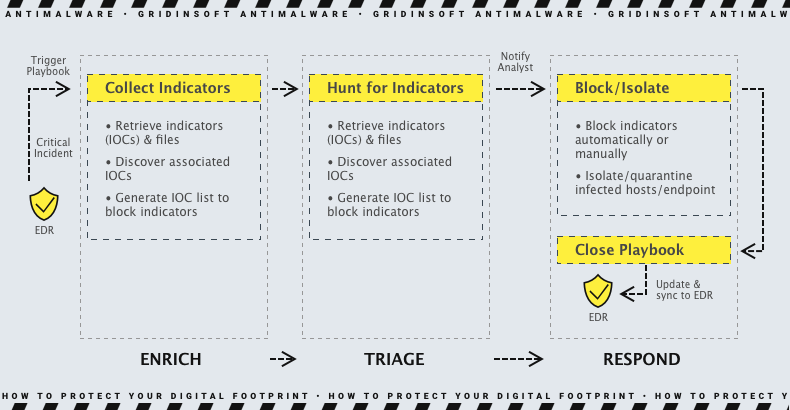
Response to Zero-Day Vulnerabilities.
Zero-day exploits cannot be identified by traditional signature-based anti-malware systems. However, a few ways to identify suspicious behavior indicate a zero-day exploit. Anti-malware vendors provide statistics on detected exploits, which can be fed into machine-learning systems for current attack identification. Signature-based detection uses digital signatures to identify variants of prior attacks. Behavior-based detection alerts for suspicious scanning and traffic on the network. A hybrid approach combines all three methods for more efficient zero-day malware discovery.
In addition, you can use EDR solutions against zero-day vulnerabilities. EDR/XDR solutions detect and respond to advanced threats, including zero-day vulnerabilities, using techniques like behavioral analysis, threat intelligence, anomaly detection, sandboxing, and rapid response. They help identify abnormal behavior patterns, attack indicators, and potential exploits while minimizing impact and awaiting a patch or remediation.
Managing and protecting your business’s digital footprint must be a priority in this dynamic digital world because your company’s overall growth and survival depend on it. The tips above will help protect your company’s valuable digital footprint from the increasingly sophisticated risks of the digital realm. Businesses must have a holistic view of their digital footprint and threat landscape. They must always consider what information is available, where it is, who can see it, how it is protected, etc. Threat awareness is an essential part of a strategy to eliminate malicious cyberattacks.

