Ransomware is considered as one of the most dangerous viruses. Companies are afraid of losing their data, so they try to do their best, spending a lot of money on security improvements. But what if I tell you that any anti-malware software which has its detection databases updated constantly is able to deal with 95% of ransomware samples?
Such a fact goes against the common imagination about ransomware attacks. Is the last one wrong? No, rather obsolete than wrong. The ransomware attack model was really close to what we imagined, which was fixed in a great number of reports, articles, and other literature. But since 2019, the attack vector has changed sharply.
What’s new in ransomware?
Since its appearance in 2013 in the shape we used to see, ransomware was a virus that was distributed chaotically, without any strict targeting. Of course, ransomware developers were not able to maintain such a massive distribution campaign, so there were a lot of offers in the darknet where you could become a part of a ransomware injection scheme. “External” people used in this scheme meant a lower operating margin (if we can call it so) and lower fault tolerance.
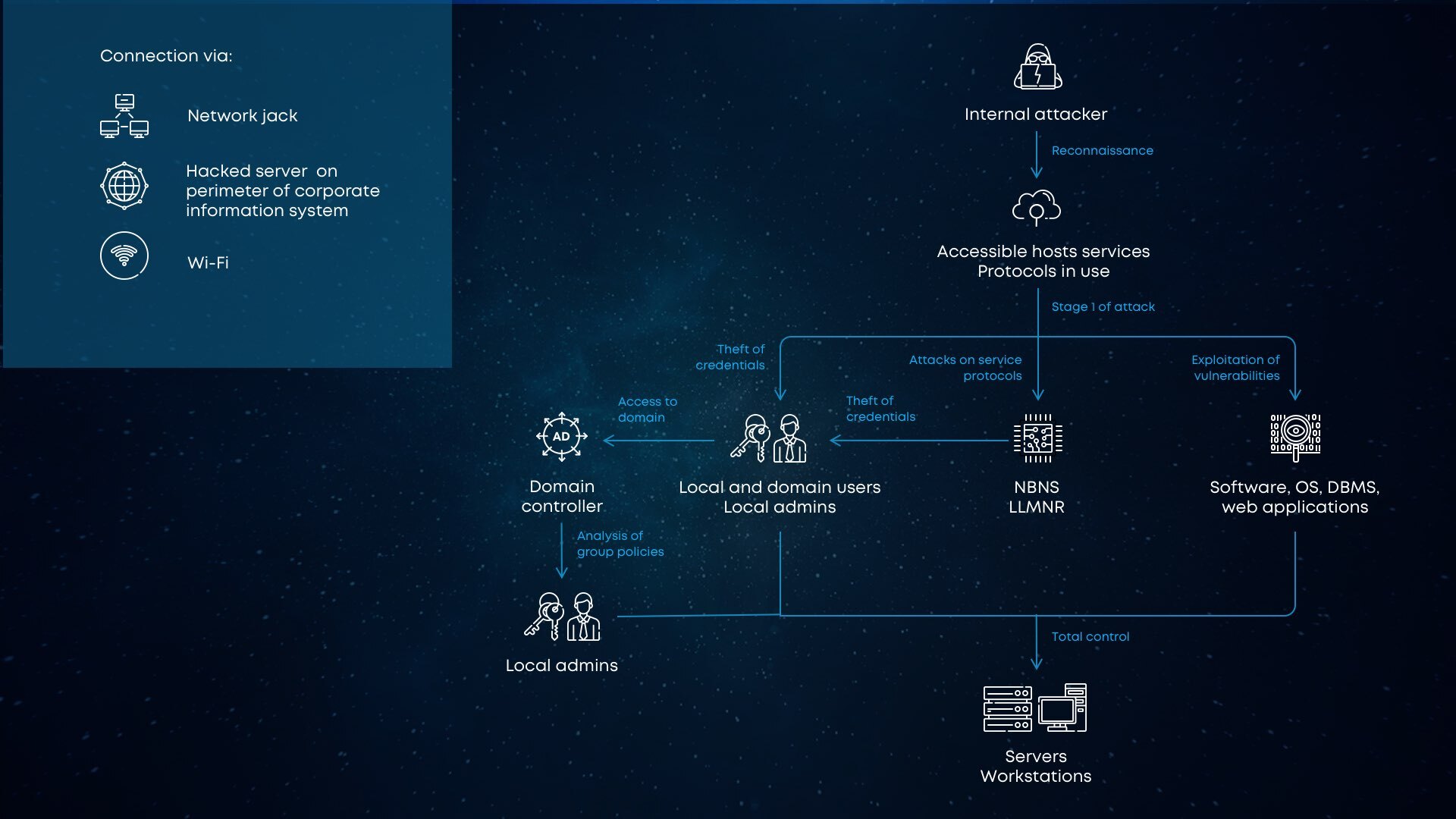
Company-specific attacks were first detected long before the massive cases of ransomware targeting. But the separated ransomware families that are used only against the companies (and likely never used to infect individuals) became really significant only at the edge of 2019. The distribution methods of such a “new” type of malware are exactly the same as other ransomware uses. But a significant difference appears after the injection: ransomware may be inactive for a long period of time – the average is about 56 days. What do cybercriminals do through this time?
The answer is easy and complex simultaneously. Global answer – they make the infected corporate network much more accessible for other viruses and for more wide ransomware spreading. The detailed answer requires to be shown in the list:
- Inspecting the network to understand the weak spots and figure out which computers/servers encryption will be more harmful to the target company.
- Injecting the additional malware that allows getting more control over the infected network, and decreases the chance of detection of ransomware by antivirus programs.
- Collecting the important data about the attacked corporation, that may be sold in the darknet in the future – credentials, interim financial/operational reports, balance sheets, etc.
- Checking the used backup mechanisms to make specific changes in the ransomware mechanism to make the usage of the backup impossible.
Several more words about the security corruption after the injection. The first infected computer can be used to spread the malware through the whole computer network. If that PC has no antivirus software onboard and has an administrator account, ransomware developers may easily get the passwords of the whole network using the hack tools. When such control is obtained, cybercriminals are able to disable the security tools on all other computers in the network, so they will not notify anyone about the malicious items onboard.
Ways of ransomware penetration
The mechanism of ransomware spreading through the network is quite clear, but what about its initial injection? As it was mentioned, corporation-targeted ransomware uses the same distribution methods as other ransomware families. There are two ways that are the most popular and were established not so long ago – email spamming and dubious applications. And while the second method may raise the suspicion of system administrators, the email letters are usually considered as something legitimate.
Human error plays a key role in such attacks. Someone who has the administrator user account gets a letter that looks like some internal documents of the company – invoices, consignment notes, approvals of operations or so. He or she will likely not ask anyone if this letter is really awaited, and just open it, injecting the ransomware.
There is also another method, that needs no counterparty inside of the company. The network vulnerabilities, together with weak passwords can give the cyber burglars a chance to do everything they need without any accidental help from the inside of the company. Ransomware distributors may just scan your network for remote-desktop protocol, which is enormously vulnerable, and hack it using brute force.
How to make your corporate network safe?
There is no universal answer to this question. The list of proper measures depends on tens of factors that differ from one company to another. There are also a lot of actions that are essential for cybersecurity, however, not all of them are implemented properly, or even not implemented at all.
First thing you need to think about is the decrease in possible damage after the malware attack. Dividing your corporate network to segments allow you to risk only a part of workstations and information that is stored on them, instead of risking all machines simultaneously.
Then, you need to deal with a massive amount of work for making your network less exploitable. The first and obvious thing for this purpose is closing all possible exploits that surely exist in your system. Remote desktop protocol, Windows Script host, local user profile, MS Office macro sets – all these things are used actively by cyber attackers. Not all of them may be closed, but at least you can force the user to enter the password when he/she tries to launch the exploitable thing, to force this person to think twice. Another thing you can do is take care of installing every security patch for the computer network as soon as possible, to be sure that you will not get your network corrupted because of holes in your network settings.
Minimizing the chances of human error is the last and the least clear among others. The clearness is caused by the presence of a human, who may unintentionally say a password or other credentials, being drunk in the bar at night on Friday. Hence, it is better to restrict the access of users to the corporate-importance credentials and make them very long and hard to remember, so even the “spy” will not be able to carry too much information. Antivirus software on every PC that has contact with mentioned important data is also a thing you need to take care of. The less the chance of a keylogger/stealer launching – the fewer the chances of a successful attack.